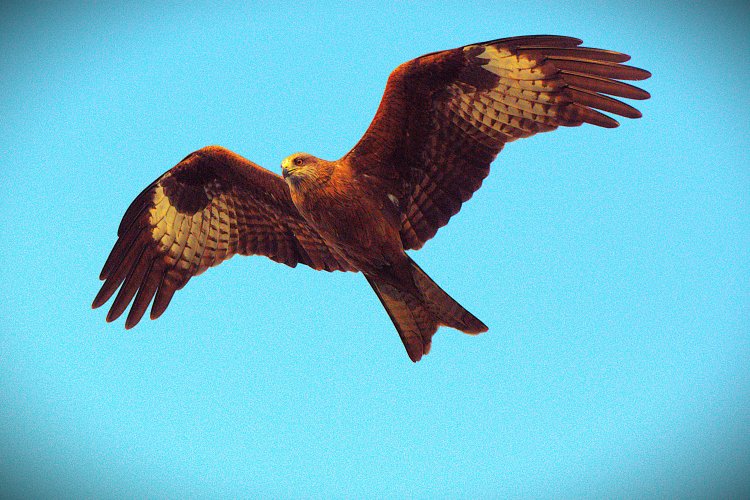
Dachigam - Where Kashmir Stag Hangul Graze in Peace !
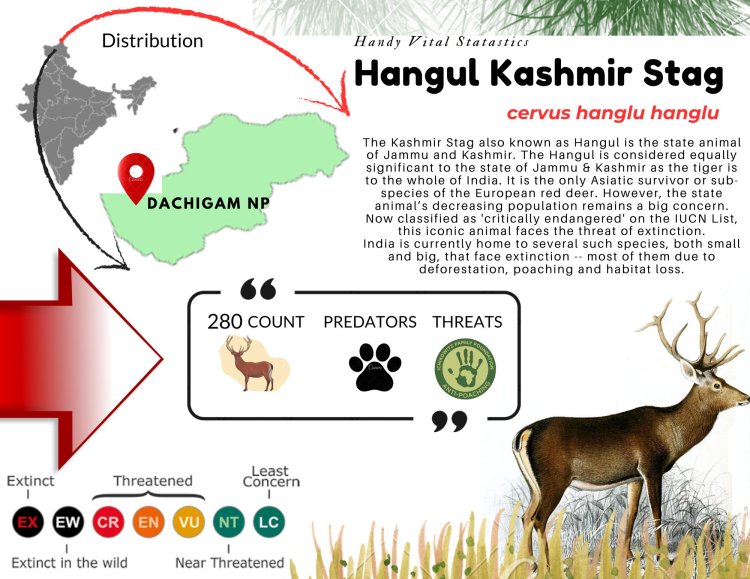
In Spite of nature's beauty, Kashmir is blessed with amazing animal species too. Among them the hangul - Popularly known as Kashmir stag, a herbivore and highly shy, sensitive animal of the deer family is a special one ! The majestic animal endemic to Kashmir, a subspecies of the Central Asian red deer and is the state animal of Jammu and Kashmir has been declared as Critically endangered and is on the verge of extinction. About 10 villages has been relocated for its protection. It's Dachigam !.The sole surviving habitat which is pride of Kashmir !

The Chillai Kalan , a 40 days period of severe winter in Kashmir was just coming to an end.The predictions of seasonal snowfall by IMD seemed to vary due to changing weather conditions.Though it was a misty morning and chill weather, but it still seemed of no luck either. Armed with binocs , i myself with 2 other companions were trudging through foggy laden grasslands.The call of Blue Whistling thrush for company along gently flowing Dagwan river. " The winter visitor Orange Bullfinch too did not show up this season which was one of rare visitor " added our guide Shabir. I was at Dachigam , which is one of less known National Parks of India, home to Critically endangered species known as Hangul - A Kashmir stag.
Located in Srinagar in Jammu & Kashmir.

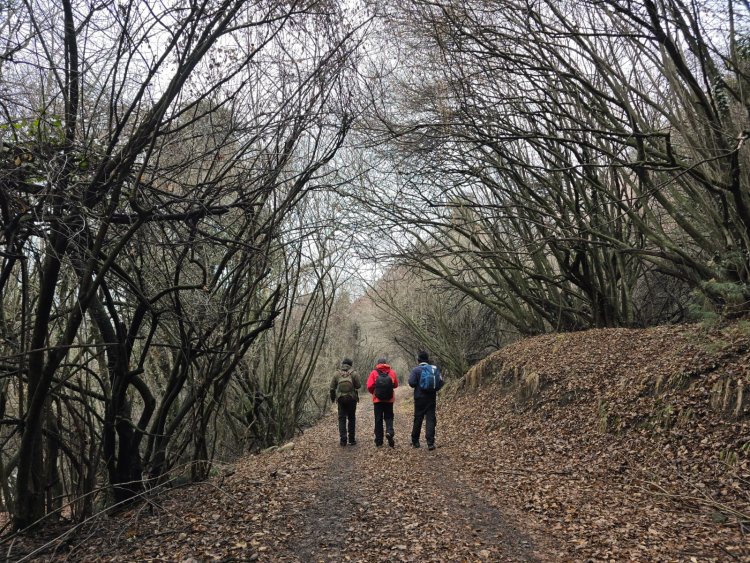
Though a battery operated vehicle is provided by forest department to travel a distance of 3 kms from the main entry gate.We preferred to walk inside the park at ease.The National parks name Dachigam that covers a core area of 141 sq km literally means 10 villages which were relocated in 1910 and has been protected area since.The park is divided in lower and upper dachigam considering altitude and terrain.

We could see the oak, horse chestnut trees and chinar trees planted by Maharaja Hari singh to supplement shortage of food during winters for inmates of National park.
Brown Fronted Wood Pecker
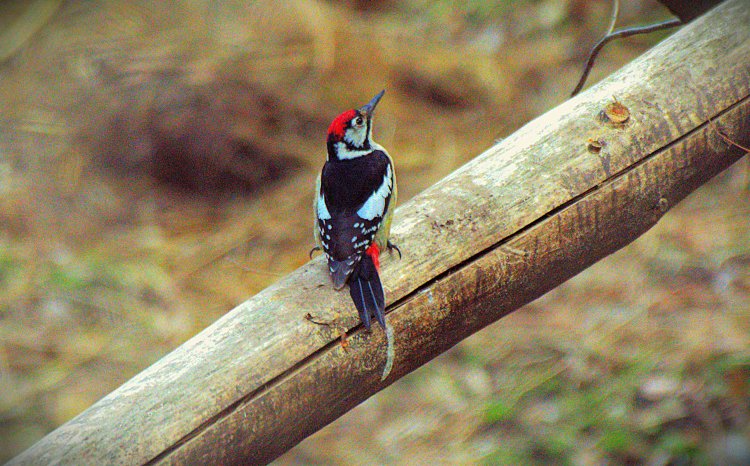

We could spot few birds which included Chestnut thrush, Gold crest ,Black throated thrush ,Black throated bush tit ,Little forktail ,Spotted forktail ,Lemon rumped warbler,Himalayan woodpecker ,Brown fronted woodpecker ,Brown dipper,and Bar tailed tree creeper
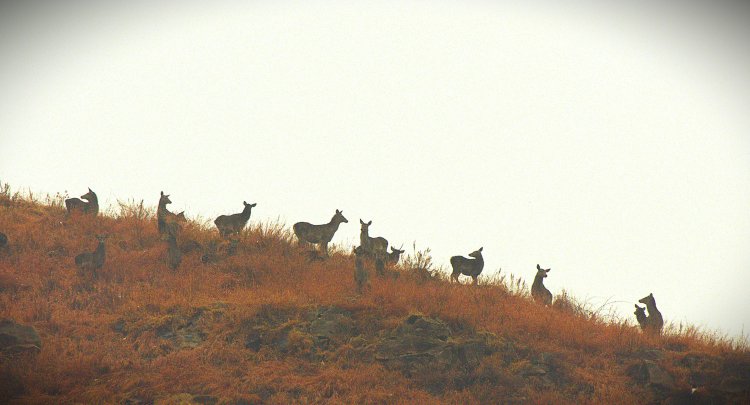
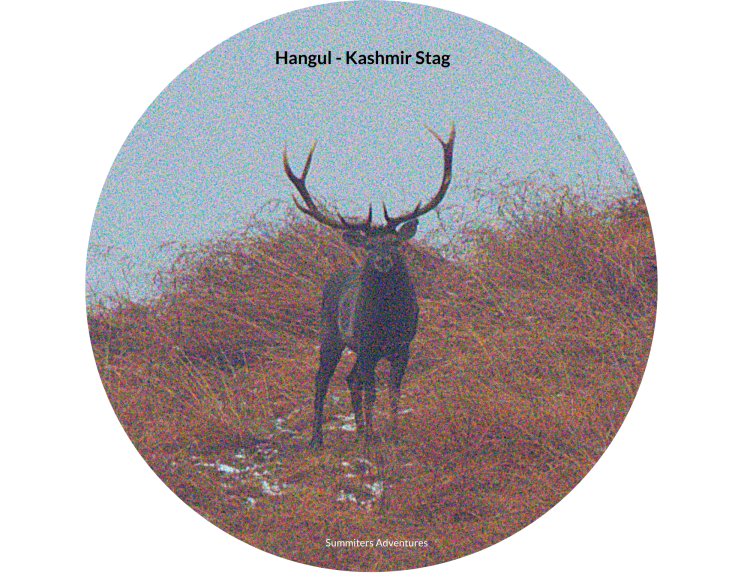
 The thick veil of mist lifted slowly at half past 10 am, we could spot a female and male hangul high above in the sky line in its natural habitat.The path interwined with thorny bushes was like a jig saw puzzle to manovouer.Our guide mentioned that it was the first sighting of the season.The male sported a 9 point antler and looked elegant.
The thick veil of mist lifted slowly at half past 10 am, we could spot a female and male hangul high above in the sky line in its natural habitat.The path interwined with thorny bushes was like a jig saw puzzle to manovouer.Our guide mentioned that it was the first sighting of the season.The male sported a 9 point antler and looked elegant.
Though the park is teeming with thick vegetation, flora and fauna including apricot,walnut,chestnut,oak,willow,wild cherry pear, poplar, plum,peach,chinar,birch, pine and elm.The department feeds vegetables for the hanguls with salt and vegetables at the water body during harsh winters.After if snows in higher altitude ,hanguls descend the slopes in search of green grass.The shy creatures settle in the grasslands and never descend if they feel insecure forever.
As per guides instructions we observed the hangul family from a distance and decided to take a detour and watch them from a distance.We could hear the calls of the Male hangul, as we traveresed the ridge behind the grassland.The herd had moved to other hill and resting during afternoon.We could see them, they were watchful !
Artistic Antlers - A Pride Possession of a Stag !
Whats the reason behind to shed ?

- Reproductive Strategy: Antlers are primarily used by male deer i.e. stags during the breeding season (rut) to compete for mates. Shedding antlers after the mating season allows the deer to conserve energy and resources for survival, especially during harsh winter months.
- Hormonal Changes: The process of shedding antlers is regulated by hormones. After the breeding season, testosterone levels in male deer decrease, leading to the breakdown of the tissues that attach the antlers to the skull. This results in the antlers falling off.
- Growth and Renewal: Shedding allows for the growth of new antlers each year, which can be larger and more robust than the previous year's. This is advantageous for attracting mates, as larger antlers are often favored by females.
- Survival Adaptation: Retaining antlers year-round would be energetically costly and could hinder mobility or survival during winter when food is scarce. By shedding them, deer can better adapt to their environment and focus on survival. The points on a deer's antlers are called tines , and they branch off from the main beam. The number and size of tines on a deer's antlers is determined by genetics, nutrition, and age.















